Talk Wellington and Island Bay cycle way
-
-

Smoother bussing and safer biking in Newtown? Now, or maybe not for a decade!
- Talk Wellington
- If you want a decently bikeable and more bus-friendly route between Newtown centre and the city, anytime within a decade, you need to give this a cheerful positive shove, now! Window closes this Wednesday! We have a partial separated cycleway and partial dedicated bus lanes in Newtown. Yes, you’ve probably submitted supportively on this before...
- Accepted from Talk Wellington posts by feedreader
- Tagged as:
- newtown
- island-bay-cycle-way
Newtown, Wellington, Wellington City, Wellington, New Zealand (OpenStreetMap)
-
-
-
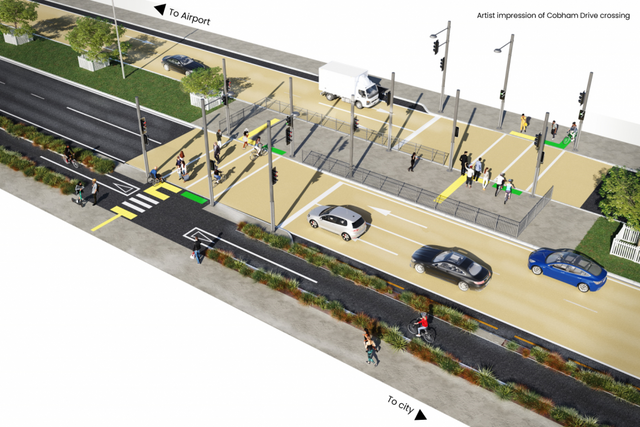
“See you in court!”: Cobham Drive, community groups, and judicial review
- Talk Wellington
- Posturing aside, what does it really mean for someone to legally challenge a roading authority’s decision – be it a cycleway, a road expansion, or a pedestrian crossing on Cobham Drive? “See you in court” – again Wellington Airport’s declaration of intent to torpedo a pedestrian crossing on Cobham Drive is fresh, but recently there’s been a...
- Accepted from Talk Wellington posts by feedreader
- Tagged as:
- cobham-drive-crossing
- island-bay-cycle-way
Cobham Drive, Kilbirnie, Wellington, Wellington City, Wellington, 6021, New Zealand (OpenStreetMap)
-
-
-
Transitional? Transformational!
- Talk Wellington
- With the “transitional cycleways”, Wellington’s using a better method to make roads safely bikeable. And when you’ve got a joined-up bikeable network, something amazing happens In case you’ve forgotten (it’s been a busy few weeks), the Transitional Cycleways are key routes… whose streets and roads were selected and confirmed with last year’s consultation based on...
- Accepted from Talk Wellington posts by feedreader
- Tagged as:
- consultation
- island-bay-cycle-way
-
-
-

A bikeable Wellington: finally the wheels are turning, give it a shove
- Talk Wellington
- After becoming a byword for cycleway SNAFUs, Wellington has been quietly getting its act together. Now a big step forward: a network, principles and who it’s for. Submit to help get the wheels turning – by 14th Dec! We promise, no more bike-related puns! Submissions are due soon – Tuesday 14th December (just before the...
- Accepted from Talk Wellington posts by feedreader
- Tagged as:
- island-bay-cycle-way
- consultation
- paneke-pneke
-
-
-

A city with a vision? AKL x WLG
- Talk Wellington
- Wellington’s got a lot of bustle and noise (Let’s Get Wellington Moving – Spatial Plan – new subdivisions – convention centre – library) but where’s the coherent vision? Hey Auckland – can we learn some things? The Wellington Urbanerds invited some insightful Aucklanders to talk about the Auckland City Centre Masterplan (CCMP) because it’s getting a lot of positive interest in nerdy circles nationwide, and we thought “Wellington needs one of those to galvanise our progress!” But it turns out that the CCMP is not the cause of Auckland’s progress – it’s a milestone marker of a bigger evolution in Tāmaki. Auckland City Centre’s chief urban designer George Weeks was insightful, visually engaging and occasionally very funny. Auckland city centre’s chief transport designer Daniel Newcombe injected insights that were pithy and thought-provoking. All up it’s worth watching the video – details at the bottom. But this post has some of the big insights for Wellington that we took away. Hat tip to Charles Dawson for invaluable note taking. A galvanising vision, with a strong whakapapa What makes the CCMP unusual as an official planning document, Weeks told us, is that it’s not “a planner’s plan” – 2,000 pages of vision down to prescriptive requirements. Instead it’s “the brochure for the city centre”. He told us that “with the 2012 CCMP, we thought it was better to have a 200 page document that 10,000 people see, or at least have skimmed, than a 2,000 page document that 100 people read in detail. We have used this approach to shape the 2020 CCMP.” It has had a major refresh in the last 8 years and the 2020 version is quite something. Galvanising vision Weeks took us through how the updated CCMP works: how it delivers on the Auckland Plan’s promise of life in Auckland, through the city centre’s form and function. It’s worth laying these out because while we definitely have bits of the formula, there’s some powerful elements we’re missing. Experience of being there The Auckland Plan (essentially the Tāmaki-Makaurau 30-year plan) sets out ten Outcomes for the city – effectively the promise of life experience that you should get, being in Auckland. The whole super-city is supposed to fulfil these promises, and the city centre’s no exception. In the CCMP, the ten citywide Outcomes or life promises are intertwined with eight place-specific Transformational Moves. The latter are the major initiatives to change the physical environment of the city centre so it can deliver those outcomes – the good Auckland experiences – for anyone who’s there. A lot of this has come into the 2020 CCMP thanks to Access for Everyone (A4E), the city centre’s transport programme done to support the CCMP refresh process (more on A4E later). Street forms and place shapes… So the 2020 CCMP has street explainers that show – conceptually but with a lot of verisimilitude – the components of the streets and buildings, the overall shape of the whole public realm that’s needed for the city centre to give people that great experience. a generic “transit street” explainer – from the CCMP These explainers are conceptual, but are tied enough to specific places, that everyone can see the trajectory of how their specific bit of the city will be changing, but crucially they can see a really solid why. …because This means “X street, and its environment, should have Y shape and form because…”. We saw, for example, that one of the biggest streets in the Learning Quarter, Symonds Street, will be a transit street for all these reasons: Symonds St, for example, needs to become a transit street not because of some abstracted notion of “sorting out the transport” but because it is at the heart of Auckland’s city centre universities, and “transit street” is the form for Symonds Street that will let it best serve people in the Learning Quarter with the good experience the Auckland Plan promises. Weeks flicked through a few examples of how the CCMP is signalling change to the built environment of Tāmaki’s city centre (which is pretty interesting – have a play here, the 2020 version is fully digital!) Our impression of all this was that the CCMP, thanks to the Auckland Plan and Access For Everyone (the transport dimension), has pretty well integrated two things that any self-respecting city needs to integrate. This is the roles of movement (transport) and place or exchange (destination activity) in any given area of the city centre. And Auckland manages to integrate these with a nice clear Why and Because for each set of changes. [Hold on, is that anything special? We know about this stuff… This tight integration – of form to function, place with movement, built form to people’s lived experience – seems pretty elementary for self-respecting cities. And you’d be forgiven for assuming Wellington has that integration in place. Indeed, things like the street concepts in Auckland’s 2020 (refreshed) CCMP don’t look too dissimilar to what LGWM put out for the Golden Mile. And the material coming out from LGWM and the Central City elements of the Spatial Plan and Wellington 2040 use a lot of the right words. Golden Mile concept from LGWM But in listening to Weeks’ presentation, we realised just how explicit and unequivocal the CCMP and A4E are about the why, the because for the physical city changes they describe, anchored home to that lived experience promised in the Auckland Plan. And the locked-in coupling between the place / destination train and the movement / transport train so they’re pulling each part of the city in the same direction towards that better experience for all Aucklanders. This coupling is something we’re muddling around in Wellington. We’re hedging our bets on saying explicitly what lived experiences we want to prioritise and privilege in our city centre. This means the transport planning and place planning are making (at best) vague bows in each other’s direction, with lots of hedging our bets about whether and how we’re prioritising “drive-through” vs “go-to” in our city centre. OK back to the presentation…] Galvanising and enabling Weeks told us that in the CCMP, when you combine the Auckland Plan’s Outcomes and the CCMP’s Transformational Moves, the product is the city centre “Opportunities”. Opportunities are projects, quite specific things, and there are quite a few listed. click on the image to have a play in the CCMP Opportunities But they’re not a set of business-case investments that clamp tunnel-vision onto ambition. They seemed to be as much illustrating the kinds of projects that would make the city centre better at giving people that great experience of Auckland living. As Weeks emphasised: “anyone can come up with an Opportunity”. (We imagine the galvanising could run like this… Hello, I’m a developer looking at buying or developing neighbouring Building X and Building Y, I can see the direction of profitable change and unprofitable change that I could make to that property, given the trajectory of change in its environment. And I can make up a project that creates a much better laneway space between them, plus better delivery access, better stormwater handling, and augmented residential-plus-commercial uses… This bundle of investments will make me money, and enhance really well that little corner of the city – so public investment and other private are likelier to come join me… ) CCMP’s generic laneways explainer (click to expand) Lesson for Wellington: let the vision be the vision, get other activity making it reality A big lesson for Wellington, Weeks said, was to “be clear about what different plans are to do. The City Centre Masterplan sets the vision, which allows many actors to work out how to deliver its different facets, or to develop their own ideas too.” The CCMP is only the green-circled bits in this picture. CCMP: a strong whakapapa The CCMP’s technical pedigree is strong – it makes good application of internationally-accepted principles of urban physics and urban dynamics. But – as Weeks put it – if the CCMP can “see further, it’s because [it is] standing on the shoulders of giants”. Complementing the CCMP’s technical pedigree is its collective human ancestry: the people, organisations, and relationships that have coalesced around it, the support that it’s known and seen to have, and the mana that this contributes to its strong legitimacy and mandate today. From the presentation a few points stood out on each of these… The technical pedigree of the CCMP Weeks and Newcombe gave us a whistle-stop tour of the set of transport and urban planning documents of which the 2020 CCMP is the progeny. Auckland Unitary Plan – The supercity’s first joined up District Plan, the “rulebook” for implementing the Auckland Plan. Forced much more collaboration in planning, for everything. City Centre Future Access Study – NZTA, Ministry of Transport, Auckland Council, Treasury, Auckland Transport found the City Rail Link would blitz all other 46 options for getting people to and from the city centre. The City Rail Link (CRL) – an underground railway link turning the city centre heavy rail terminus into a through-station, building 4 new underground stations. Doubles the number of Aucklanders with 30min access to city centre. After years of arguing, finally underway once tax was to pay 50% (thanks ATAP). Auckland Transport Alignment Project (ATAP) (2016-17, updated 2018) Auckland-region-wide (not just one bit) merit-based priority list of all the big-ticket transport projects, costed and agreed by all funders and deliverers. Crucially: first acknowledgement by central government that Auckland couldn’t road-build its way out of its traffic problems Business Case for Walking – first quantification of the value of city centre walking to Auckland’s economy, done in 2017. [Hey “walkable capital”, where’s ours?] The creation of documents always sounds more coherent in retrospect, but Weeks and Newcombe emphasised that it’s not been a nice clean sequential progress. Key principles of urban physics (like the role of people walking) have only been given oxygen relatively late in the sequence. The need to get tax funding to co-fund megaprojects has meant a lot of back-and-forth raruraru with central government, and between the various bits of Auckland’s council family. And some great documents – like the Business Case for Walking mentioned above – have no official legal weight: a decision-making body can completely ignore them if it wants. But we heard that the various documents have meant that amongst the bureaucracy and other government power-holders, there’s been an accumulation of key principles of good urban physics, akin to accumulation of organic matter. Sometimes it’s just leaves falling, but sometimes there’s a large trunk. These accumulations in the establishment’s hivemind make it much harder to go back and relitigate, as there’s been some crystallisation in the thinking. (Though, of course, as Newcombe noted, that doesn’t stop people trying!) Access for Everyone – the complementary transport element of the City Centre Masterplan which was developed as part of the CCMP refresh – is a great example. In traditionally car-mad Auckland, the entire Auckland Council voted unanimously to begin A4E trials “enabling a decisive mode shift away from private vehicles, to make better use of finite city centre space and improve the quality of the environment.” Wow. Access For Everyone’s car-free Queen Street / Horotiu Valley with Low Traffic Neighbourhoods around. And no more driving through the city centre! The human side of CCMP’s whakapapa We heard that a major benefit of the sequence of documents was the relationships and conversations that a document creates a pretext to have. There’s been a lot of investment in behind-the-scenes engagement, with big stakeholders in the city. This has paid off in an unusual level of big players’ trust and buy-in to the vision and the big moves to get there. From large developers, through Heart of the City (the inner city Business Improvement District), through the AA, NZTA, to the City Centre Residents’ Group (fun fact: 40,000 people live in Auckland’s city centre alone). This good stakeholder engagement bears fruit: it enabled councillors to support the 2020 CCMP relatively easily, despite it having relatively little engagement from the wider public (a few hundred submissions compared with the Unitary Plan’s ~10,000). It’s not a coincidence that Precinct Properties has seen fit to drop a billion (with a B) dollars of its shareholders’ money into the Commercial Bay development – Weeks observed that it’s on the strength of the new trust and joined-up thinking developed through the CCMP process. Daniel Newcombe spoke from experience about the collaboration that had eventually started to come, once “you can get people to stop introducing competing plans” and come together. Sometimes this requires biding your time, working by osmosis, and finding the sensible individuals in an organisation on whom to work, and building coalitions that chip away at antipathetic organisations. Getting people to issue formal letters of support on behalf of their organisations can be extremely powerful, he said. Iwi influence We heard that one major improvement of the 2020 refreshed CCMP over the 2012 original is the inclusion of Māori outcomes. For the refresh, the ADO worked closely in partnership with Auckland’s Mana Whenua Kaitiaki Forum to develop a Māori outcomes plan. This work shaped Transformational Move 1: Māori Outcomes, with proposals for a papa kōkiri at the waterfront and a whare tāpere at Aotea Square. The 2020 CCMP manifests the Auckland Plan’s Māori Identity and Wellbeing outcome and Te Aranga Māori Design Principles via Outcome 1: Tāmaki Makaurau – Our place in the world. It sets out the big interventions and systemic changes to bring mana whenua presence, Māori identity and life into the city centre and waterfront. There are some big-ticket, high-visibility things and pervasive, interwoven ones. To our (Pākehā) ears this sounded pretty great… Attack of the roadcones! Plans are essential, but how do you get them going, especially when there’s so many large, cumbersome players with inertia? Weeks had peppered the presentation with cool before-and-after shots of some iconic Auckland changes, including Te Ara i Whiti / the (pink) LightPath, and localised street improvements like our favourite, O’Connell Street (below). O’Connell Street. oh.yes.melbourne We know (though the webinar didn’t go in depth here) that much of Auckland city centre’s evolution that you and I can see today was driven by the Auckland Design Office, with Auckland Transport and Auckland Council partners. Their projects opened people’s eyes to how good street change could be done, and that actually the good “urban physics” did apply in Auckland too. And they gave Auckland council family a chance to practice delivering street change together, and figure out how it can be done without anyone losing an eye. They did it with a combination of a figurehead / champion / lightning rod / air cover for the ground troops (AKA Ludo-Campbell-Reid) plus a ninja team of designers, engagers and doers, doing on-the-ground projects that brought to life the good practice of urban design. Projects like Fort Street, O’Connell Street, Fort Lane, and Jean Batten Place showed that – contrary to received wisdom – replacement of on-street car parking with high-quality streetscape was good for business. Collaboration with Auckland Transport led to the creation of a pop-up cycleway along Quay Street (well before the Innovating Streets for People pilots) which is now being incorporated into a permanent street redesign that will finish this year. It’s not been an easy road: by now, ten pilots of the street changes for Access for Everyone were supposed to be underway, following that unanimous Council vote, but just one (High Street) has been. And the ADO has now been disbanded, allegedly due to their irritating conservative parts of the establishment with cost-cutting as a pretext. But there’s momentum now… Auckland’s changing, and has lessons for us Throughout the session the Zoom chat pane had been running hot with questions and comments from the “floor” (aka the online audience). Weeks and Newcombe took questions from the pane and from the Urbanerds presenters, and a few highlights stood out including lessons for Pōneke… Lesson for Wellington: get partners on the same transport page Weeks’ and Newcombe’s first lesson was to get a multi agency agreement on transport together. It can’t just be the city council or regional council. It has to have central government buy-in; they can’t be pulling in the other direction from the city or region with their ambitions for the city’s transport. Updated ATAP, with all the partners This consensus shifts the conversation from “Do we need that good stuff replacing the bad stuff?” to “When do we need it?”. You have to keep the focus at that “when” level, not allowing relitigation of the fundamental principle of urban physics that you’ve achieved consensus on. We wonder: is this LGWM? Is it shifting our conversation? Is NZTA pulling in the same direction as the city, as the regional council? Lesson for Wellington: generate the brochure, together A second big lesson is that you have to have the vision, the brochure, the clear picture of the good life that your city wants to give everyone who’s in the city centre, whatever they’re doing there. This has to be the rationale for any the physical changes that you entertain or consider. The Auckland Plan’s 8 outcomes – promises of the experience of life in Auckland, that the CCMP too must deliver This “brochure” must be developed hand in glove with the actors we want to be supporting it, building on any public mandate you already have but not driven by the wider public. This conversation with the big players should not feel like it’s led by any one player (developers, or transport-planners, or inner-city-residents, or businesses – nor even, we wonder, council?). What it must be is very good quality engagement that builds a strong trust and instils a foundation layer of commitment to (or at least grudging acknowledgement of) solid urban physics, and the trajectory of change needed throughout the city. Lesson for Wellington: CBDs are doomed Listener Sally asked whether a focus on a city centre had been overtaken by COVID and its boost to working from home, and localism, especially in Wellington where there’s such a large commuter population. Weeks’ answer put it in much more professional terms, but the message came through clearly: if your city centre is mostly a Central Business District, where “business” is the dominant activity, it’s doomed. Monocultures always make a system vulnerable to shocks, in agriculture, horticulture and in cities If it’s a central city, with a hundred or a thousand different reasons for people of all different walks of life to be there, then it’ll be fine – it’ll change and adapt, but the power of people wanting to be there is the lifeblood of a city. “The death of the city has been predicted since the invention of the city, in the Bronze Age” Weeks observed – “and if you’ve got an actual city, it won’t happen.” We wonder… how much of Wellington’s central city is a dead zone by 6.30pm? How much are we reinvigorating and diversifying the reasons to be there? Lesson for Wellington: lock all good plans to something with teeth Weeks emphasised that the power of these plans comes from linking area plans and other non-statutory plans to ones with statutory power. So despite being a non-statutory document, the City Centre Masterplan carries weight because they mapped its outcomes tightly against the Auckland Plan (the statutory 30-year plan for the whole city) and councillors have voted overwhelmingly in favour of it. diagram showing how the CCMP is making good on the Auckland Plan’s promises, in the city centre We definitely don’t yet have the vision and its trust, nor the solid hook between statutory and non-statutory … but we have some elements of the recipe. We wonder… how much of the CCMP-style whakapapa do we have, if not the actual document? Could we build these levels of trust and vision together? Some Wellington City Council planning and design gurus attended the session and helpfully fielded some questions about where Wellington was at. Our one-liner summary was: it’s not going to hell in a handcart, but it’s definitely all up in the air. Smart engagement from Urbanerds listeners and Talk Wellington readers is really needed. We’ll pick up “so what for us?” in the next post. Here’s the video: link, passcode SUa&tOC5 Meantime… where have you seen signs of a clear vision of good Wellington city life, for everyone?
- Accepted from Talk Wellington posts by feedreader
- Tagged as:
- draft-spatial-plan
- supercity
- waterfront
- island-bay-cycle-way
- covid-19
- libraries
- convention-centre
- lets-get-wellington-moving
-
-
-

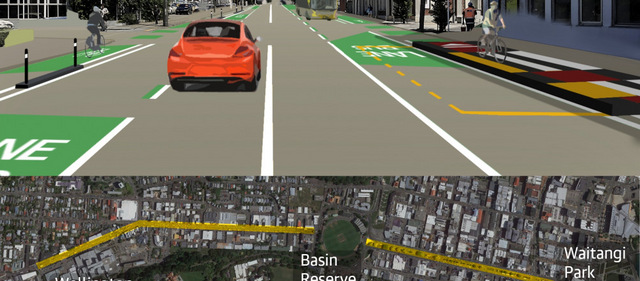
Waiting for light rail? Let’s build a busway now!
- Talk Wellington
- One question on the mind of everyone suffering from Wellington’s transport problems is – when will Let’s Get Wellington Moving actually get us moving? Guest poster Marko Garlick sees a supercharger hiding in plain sight There seem to be lots of abstract projects planned to be delivered, maybe years from now: urban State Highway 1 “improvement” with more tunnels, and a rapid (or maybe just frequent) mass transit line from Lambton through Newtown and to the Airport. But where will these actually go? And how do we deal with difficult questions about flows around the Basin Reserve? Wellingtonians waiting for new transport infrastructure to be built… Where does mass transit go? For mass transit, there are many things to consider. Is it along the waterfront quays or along Lambton Quay / the Golden Mile? Along Taranaki St or along Cambridge Terrace? Where does it go through the Basin Reserve? Many people are speculating. And the big one: light rail or trackless trams, or both? Mock-up of a route down Taranaki St What about the urban motorway? The LGWM proposal has a pretty good plan to maintain the amenity of the city above. They want to underground the motorway from the Terrace to Mt Vic. A new Te Aro park will be created on top. However people are questioning the need for more lanes created by a new Terrace and a new general traffic Mt Vic tunnel. More lanes in urban motorways creates induced demand. More lanes means make people drive more which kills off any travel savings created by the bigger road. It’s a transport strategy just as smart as trying to lose weight by buying bigger pants! Bigger roads take up valuable space and just fill up with more traffic (looking at you Auckland, thanks for showing us what not to do) This uncertainty is paralysing! Those who are in the “pro-car” camp say they like mass-transit but that must come after their bigger road. Those in the “pro-PT” camp want light rail first and a smaller road. Finger-pointing and party lines are drawn. Tough and costly decisions will have to be made about irreversible projects around the Basin. Once you make a flyover, tunnel or lay down tracks you can’t (quickly) go back. I think we can break out of this inaction and stupor with an interim middle ground: a busway. Case Study: Auckland’s Northern busway The idea for this has come from the success of Auckland’s northern busway. It is a dedicated two-lanes for buses from the northern foot of the Harbour Bridge up SH1 to Constellation Drive with world-class stations and frequent congestion-free services into the city. It has seen year-on-year double-digit growth numbers over its 11 years in service, and is being extended to Albany and beyond shortly. Eventually tracks will be laid down for a second-harbour crossing for light-rail. Radical incrementalism Initially the busway was just a narrow shoulder each side of the northern motorway. People were sceptical initially but its success was undeniable and has provided the basis for upgrades and extensions. What the Northern busway shows is that doing something now, and building on it, is more practical and politically palatable than trying to justify a massive spend up front. This is applicable to Wellington’s light rail situation. It is relatively low-cost initially, can display almost mass-transit qualities and is more flexible as progress is made towards light-rail. Why a busway? A busway is what Wellington needs now. We cannot wait another 10-15 years for a big decision on the Basin and Mt Vic tunnel. A busway will provide many benefits: It is far cheaper to implement right away and far quicker to implement (I envisage 3 years for the first stage).It also demonstrates demand for mass-transit and will allow us to see whether a certain route is a good idea or not.It also allows for land-use intensification now, providing greater density and amenity to a future light rail line. What will it look like? So what would this look like? I think that the busway should start at the train station, go along the waterfront quays, and then either go along Taranaki St or Cambridge/Kent Terrace. Ideally, it should run in the centre of street with weather protected stops and room for cycleway and signal-priority. Stops should mirror light rail ones, being spaced out for speed and reliability. Along most of the route the buses could probably hit 60km/h speeds, congestion free, all day. [Ed: just let that sink in. Congestion free. A clear run.] Separate branding would be an excellent addition. The Northern Express (NEX) is what Auckland has; the Wellington Express (WEX) is what we could have. This post is about incrementalism and the key takeaway is something half-done is better than waiting ages for the ‘perfect’ solution. If the busway is barebones at first before getting upgrades then so be it. The mess at the Basin can be avoided by stopping bus priority at the start, then resuming it into Newtown. This is what the Northern Busway does with dedicated lanes ending at the Harbour Bridge, then resuming on Fanshawe St. What the waterfront quays look like now (shudders). Hardly the “walkable city”. A thing of beauty: What a complete Wellington busway could look like The busway can be upgraded over time. Greenspace, cycleways, better stops, a possible underpass on Waterloo Quay to connect to the railway station. Summing up In an ideal world, we can all agree on the light-rail and grade-separation issues at the Basin and they may already have been implemented. But that is not the case. Although there is lots of details to work, the principle of a busway now then future conversion to higher-capacity light-rail is a sound one in my mind. Do you have any ideas why Wellington has not had bus priority – via a busway, or anything else – for so long? What do you think of fast buses in the city centre, and in the suburbs? A version of this post was originally published on TraNZport; see the original here. Image credits Cover image by Smarter TransportSkeleton waiting, original unknownTaranaki mock-up by LGWMAuckland rush hour by Getty imagesAuckland busway by Greater AucklandQuays now, screen grabBusway by AT
- Accepted from Talk Wellington posts by feedreader
- Tagged as:
- newtown
- waterfront
- island-bay-cycle-way
- lets-get-wellington-moving
Newtown, Wellington, Wellington City, Wellington, New Zealand (OpenStreetMap)
-
-
-
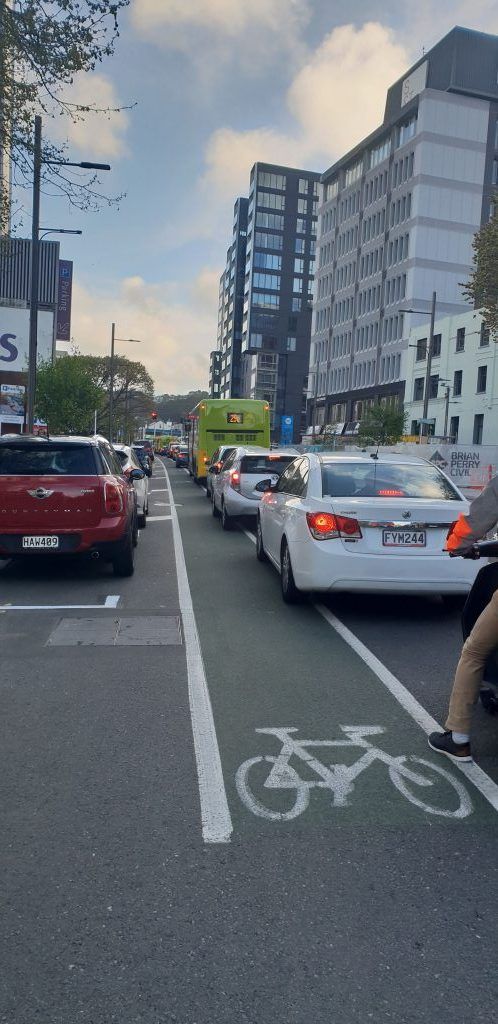

“It can’t be bad if Council keeps building it!”
- Talk Wellington
- Guest poster and nervous cyclist Barb picks up on a really interesting question in the judicial review hearing over Wellington city council’s decision to implement a parking-protected cycleway on a suburban main street.
- Accepted from Talk Wellington posts by feedreader
- Tagged as:
- island-bay-cycle-way
-


